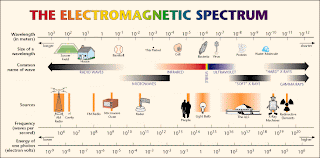
We only see a small part of the spectrum. The electromagnetic spectrum consists of radio waves, x-rays, visible light, gamma rays, and other rays, waves, and frequencies.
- Frequency- number of cycles per oscillation
- Wave- characterized by their wavelength frequency
- Ray- a beam of light or energy
The longest waves are used for radio communication, these waves are hundreds of kilometers long to about one meter.

As you progress the next waves, microwaves and infrared light, are used. Microwaves are used for cooking and communication. Infrared light is used in computers, CD players and game consoles to read disks.
Farther down the spectrum there is visible light. Visible light has the only wavelengths that our eyes can receive. Other than seeing plants use it for photosynthesis, and scientists have created lasers that take certain colors from visible light and project only that color.
After visible light in the spectrum there is ultraviolet light. The ultraviolet part of the spectrum is divided into three parts.
- Near Ultraviolet
- Far Ultraviolet
- Extreme Ultraviolet

An ultraviolet picture of the sun
The next part of the spectrum is x-rays. X-rays were discovered by William Roentgen in Germany in 1895; he discovered them by accident. The "X" stands for unknown. X-rays are used for photographing insides of bodies, and in satellites to see things in space like black holes and neutron stars which emit x-rays.
The last part of the spectrum are gamma rays. Gamma rays have the shortest wavelength and contain the most energy. They are generated in nuclear explosions and radioactive atoms. They are produced in the hottest regions in the universe. To see anything with a gamma ray telescope gamma rays have to be hit with electrons to slow them down so they don't pass through the matter in the telescope.
